The foundation of any blockchain is in its Virtual Machine.
What is a Virtual Machine and how is Elrond network’s VM different in the blockchain field ?
Essentially, a blockchain’s Virtual Machine is the computational layer of a blockchain. It allows code to be read, relayed, and executed.
It is the ‘World Computer’ component of Ethereum. It allows a blockchain to act as a virtual computer and executes smart contracts.
Elrond’s Virtual Machine, #Arwen, uses is own custom-built K Framework back end and is built on WASM.
This allows it to support three assembly languages: IELE VM (LLVM built in K), KEVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine built in K) and WASM
https://runtimeverification.com/blog/elrond-gets-new-secure-dev-tooling-and-a-formal-semantics
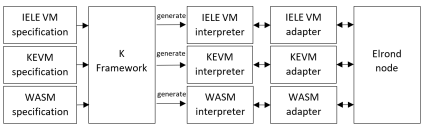
This allows Smart Contracts to be written in any popular programming language. On top of this, Arwen is Ethereum Virtual Machine EVM compliant so,
not only that a SC written for ETH will run seamlessly on Arwen, but interoperability between the chains is also achieved.
Arwen has accurate metering with configurable cost per individual WASM operation code. This means that gas fees on Elrond are arbitrary and can be changed via governance.
Meta transactions allow for gasless transactions where user on-boarding is necessary or other specific cases.
Elrond is built with assured cross-chain interoperability. There is no limit to communication channels that can be created between any other software.
By using adapters, interoperability is implemented at the VM level. SCs take custody of native tokens and issues pegged ESDTs.
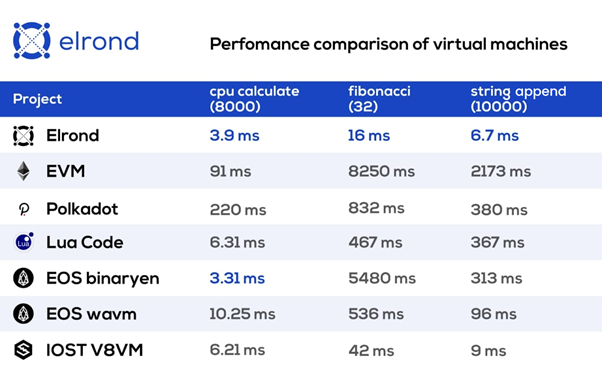
Arwen was built as fast and as secure as possible, without adding restrictions to smart contracts.
The Elrond IDE provides #developers the ability to debug contracts written in Rust, with a Rust framework that allows for efficient SC code.
BUIDL https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=Elrond.vscode-elrond-ide
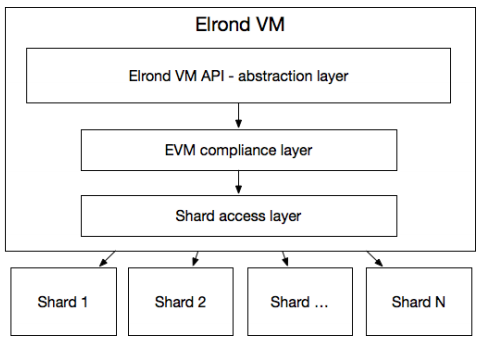
Arwen is a stateless VM. While being executed, a smart contract is not allowed to write to the blockchain, nor to its storage.
Instead, changes are applied only after execution and only if execution is successful – preventing the need for reverting operation and increasing speed.
A smart contract can be stopped by Arwen if necessary. Arwen runs in its own process, separate from a node.
The two exchange information via a collection of ‘anonymous pipes’ (stored in the emulated Random Access Memory). This increases stability and security.
Intrashard Smart Contracts can call each other with no time delay.
Adaptive State Sharding also allows smart contracts to call other smart contracts stored by a different shard (asynchronously).
This is handled by the Arwen VM so developers do not need to worry about shards.
All of this adds up to a seamless smart contract writing experience for any developer, a performant and efficient World Computer,
an interoperable chain without communication limitations, and an improved Ethereum 2.0 ready to integrate; paired with MEX's bootstrapped liquidity.
There’s no telling the limit to Elrond's capabilities. New technologies will arise as creative minds continue to build.
Many aspects of the world as we know it will be fundamentally changed thanks to the power of blockchain.
Written by @CryptoTechs
Tweet Share

You can check if you are not dealing with a scam
Check now

 @elrondwiki.elrond
@elrondwiki.elrond